When creating a file on GitHub, consider the following:
- If you try to create a new file in a repository that you don’t have access to, we will fork the project to your personal account and help you send a pull request to the original repository after you commit your change.
- File names created via the web interface can only contain alphanumeric characters and hyphens (
-). To use other characters, create and commit the files locally, then push them to the repository on GitHub. - Your repository may have push rulesets enabled. Push rulesets may block creating a new file in the repository based on certain restrictions. Push rulesets apply to the repository's entire fork network. Which means that any push rulesets that are configured in the root repository will also apply to every fork of the repository. For more information, see About rulesets.
Warning
Never git add, commit, or push sensitive information, for example passwords or API keys, to a remote repository. If you've already added this information, see Removing sensitive data from a repository.
-
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
-
In your repository, browse to the folder where you want to create a file.
-
Above the list of files, select the Add file dropdown menu, then click Create new file.
Alternatively, you can click in the file tree view on the left.

-
In the file name field, type the name and extension for the file. To create subdirectories, type the
/directory separator. -
In the file contents text box, type content for the file.
-
To review the new content, above the file contents, click Preview.

-
Click Commit changes...
-
In the "Commit message" field, type a short, meaningful commit message that describes the change you made to the file. You can attribute the commit to more than one author in the commit message. For more information, see Creating a commit with multiple authors.
-
If you have more than one email address associated with your account on GitHub, click the email address drop-down menu and select the email address to use as the Git author email address. Only verified email addresses appear in this drop-down menu. If you enabled email address privacy, then a no-reply will be the default commit author email address. For more information about the exact form the no-reply email address can take, see Setting your commit email address.

-
Below the commit message fields, decide whether to add your commit to the current branch or to a new branch. If your current branch is the default branch, you should choose to create a new branch for your commit and then create a pull request. For more information, see Creating a pull request.
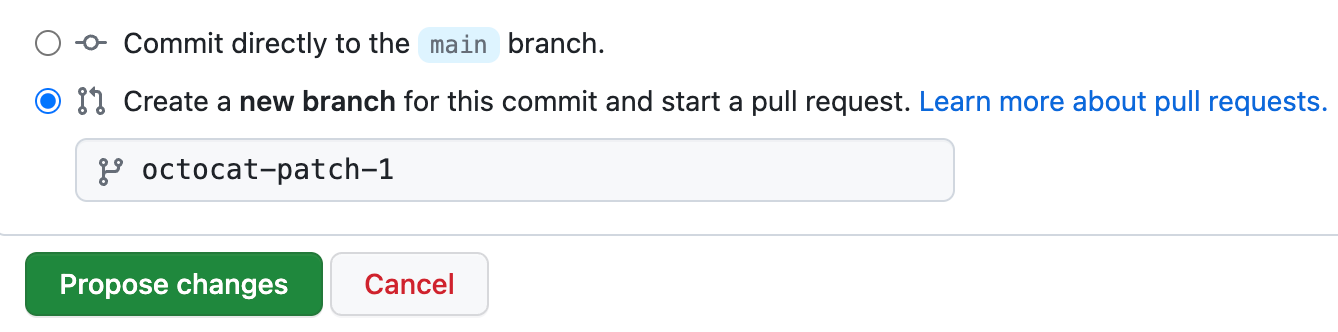
-
Click Commit changes or Propose changes.