Prerequisites
- Access to GitHub Copilot. See What is GitHub Copilot?.
- Latest version of Visual Studio Code. See the Visual Studio Code download page.
- The GitHub Copilot extension - Install this from the Visual Studio Marketplace. For more information, see Set up GitHub Copilot in Visual Studio Code in the Microsoft documentation.
- Sign in to GitHub in Visual Studio Code. If you experience authentication issues, see Troubleshooting issues with GitHub Copilot Chat in IDEs.
If you have access to GitHub Copilot via your organization, you won't be able to use GitHub Copilot Chat if your organization owner has disabled chat. See Managing policies for Copilot in your organization.
Submitting prompts
You can ask Copilot Chat to give code suggestions, explain code, generate unit tests, and suggest code fixes.
-
To open the chat view, click the chat icon in the activity bar or press Control+Command+i (Mac) / Ctrl+Alt+i (Windows/Linux).
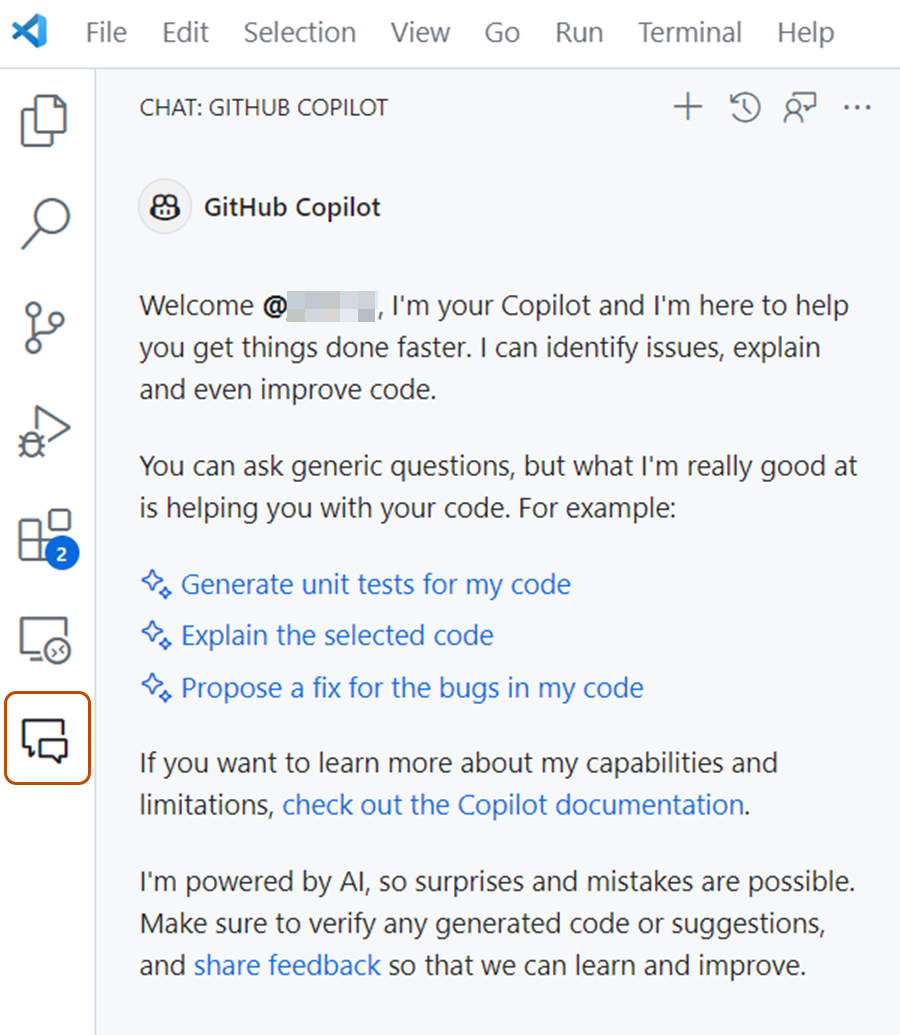
Tip
For additional ways to access Copilot Chat, including inline with your code, see Additional ways to access Copilot Chat below.
-
Enter a prompt in the prompt box, or click one of the suggested prompts. For an introduction to the kinds of prompts you can use, see Getting started with prompts for Copilot Chat.
-
Evaluate Copilot's response, and make a follow up request if needed.
The response may contain text, code blocks, buttons, images, URIs, and file trees. The response often includes interactive elements. For example, the response may include a menu to insert a code block, or a button to invoke a Visual Studio Code command.
To see the files that Copilot Chat used to generate the response, select the Used n references dropdown at the top of the response. The references may include a link to a custom instructions file for your repository. This file contains additional information that is automatically added to all of your chat questions to improve the quality of the responses. For more information, see Adding repository custom instructions for GitHub Copilot.
Using keywords in your prompt
You can use special keywords to help Copilot understand your prompt. For examples, see Getting started with prompts for Copilot Chat.
Chat participants
Chat participants are like domain experts who have a specialty that they can help you with.
Copilot Chat can infer relevant chat participants based on your natural language prompt, improving discovery of advanced capabilities without you having to explicitly specify the participant you want to use in your prompt.
Note
Automatic inference for chat participants is currently in public preview and is subject to change.
Alternatively, you can manually specify a chat participant to scope your prompt to a specific domain. To do this, type @ in the chat prompt box, followed by a chat participant name.
For a list of available chat participants, type @ in the chat prompt box. See also GitHub Copilot Chat cheat sheet or Chat participants in the Visual Studio Code documentation.
Copilot Extensions chat participants
You can also install Copilot Extensions that provide chat participants. You can install these extensions from GitHub Marketplace and from Visual Studio Code Marketplace. For information about extensions from GitHub Marketplace that provide chat participants, see Using extensions to integrate external tools with Copilot Chat.
Slash commands
Use slash commands to avoid writing complex prompts for common scenarios. To use a slash command, type / in the chat prompt box, followed by a command.
To see all available slash commands, type / in the chat prompt box. See also GitHub Copilot Chat cheat sheet or Slash commands in the Visual Studio Code documentation.
Chat variables
Use chat variables to include specific context in your prompt. To use a chat variable, type # in the chat prompt box, followed by a chat variable.
To see all available chat variables, type # in the chat prompt box. See also GitHub Copilot Chat cheat sheet or Chat variables in the Visual Studio Code documentation.
Using GitHub skills for Copilot
Note
This functionality is available with the Copilot Chat extension v0.20.3 or later and VS Code or VS Code Insiders 1.93 or later.
Copilot's GitHub-specific skills expand the type of information Copilot can provide. To access these skills in Copilot Chat, include @github in your question.
When you add @github to a question, Copilot dynamically selects an appropriate skill, based on the content of your question. You can also explicitly ask Copilot Chat to use a particular skill. You can do this in two ways:
- Use natural language to ask Copilot Chat to use a skill. For example,
@github Search the web to find the latest GPT model from OpenAI. - To specifically invoke a web search you can include the
#webvariable in your question. For example,@github #web What is the latest LTS of Node.js?
You can generate a list of currently available skills by asking Copilot: @github What skills are available?
AI models for Copilot Chat
You can change the large language model that Copilot uses to generate responses to chat prompts. You may find that different models perform better, or provide more useful responses, depending on the type of questions you ask. For more information see Changing the AI model for Copilot Chat.
Additional ways to access Copilot Chat
In addition to submitting prompts through the chat view, you can submit prompts in other ways:
- Inline: To start an inline chat directly in the editor or integrated terminal, enter Command+i (Mac) / Ctrl+i (Windows/Linux).
- Quick chat: To open the quick chat dropdown, enter Shift+Command+i (Mac) / Shift+Ctrl+i (Windows/Linux)
- Smart actions: To submit prompts via the context menu, right click in your editor, select Copilot in the menu that appears, then select one of the actions. Smart actions can also be accessed via the sparkle icon that sometimes appears when you select a line of code.
See inline chat, quick chat, and chat smart actions in the Visual Studio Code documentation for more details.
Copilot Edits
Use Copilot Edits to make changes across multiple files directly from a single Copilot Chat prompt. Copilot Edits has the following modes:
- Edit mode: Use edit mode when you want more granular control over the edits that Copilot proposes. In edit mode, you choose which files Copilot can make changes to, provide context to Copilot with each iteration, and decide whether or not to accept the suggested edits after each turn.
- Agent mode (public preview): Use agent mode when you have a specific task in mind and want to enable Copilot to autonomously edit your code. In agent mode, Copilot determines which files to make changes to, offers code changes and terminal commands to complete the task, and iterates to remediate issues until the original task is complete.
Using edit mode
- To start an edit session, select Open Copilot Edits from the Copilot Chat menu.
- Optionally, add relevant files to the working set to indicate to GitHub Copilot which files you want to work on.
- Submit a prompt. In response to your prompt, Copilot Edits determines which files in your working set to change and adds a short description of the change.
- Review the changes and Apply or Discard the edits for each file.
For more detailed instructions, see Copilot Edits in the Visual Studio Code documentation.
Using agent mode
Note
Agent mode is currently available to VS Code Insiders as a public preview and is subject to change. See Copilot Edits in the Visual Studio Code documentation.
- To start an edit session, select Open Copilot Edits from the Copilot Chat menu.
- Select Agent from the mode dropdown menu.
- Submit a prompt. In response to your prompt, Copilot streams the edits in the editor, updates the working set, and if necessary, suggests terminal commands to run.
- Review the changes. If Copilot suggested terminal commands, confirm whether or not Copilot can run them. In response, Copilot iterates and performs additional actions to complete the task in your original prompt.
For more information, see Copilot Edits in the Visual Studio Code documentation.
Vision
Note
Vision is currently available to VS Code Insiders as a public preview and is subject to change.
Vision requires that you use the GPT-4o model and upload one of the following file types: JPEG (.jpg, .jpeg), PNG (.png), GIF (.gif), or WEBP (.webp).
You can attach images to your chat prompts to help Copilot understand your question. For example, you can attach a screenshot of a code snippet to ask Copilot to explain the code, or share mockups of new designs to ask Copilot to generate code.
You can drag and drop images into the chat window, or attach them through the VS Code UI.
Sharing feedback
To indicate whether a response was helpful, use the thumbs up and thumbs down icons that appear next to the response.
To leave feedback about the GitHub Copilot Chat extension, open an issue in the microsoft/vscode-copilot-release repository.
Further reading
- Prompt engineering for Copilot Chat
- Using Copilot Chat in VS Code and Getting started with GitHub Copilot Chat in VS Code in the Visual Studio Code documentation
- Asking GitHub Copilot questions in GitHub
- Responsible use of GitHub Copilot Chat in your IDE
- GitHub Terms for Additional Products and Features
- GitHub Copilot Trust Center
- GitHub Copilot FAQ
Prerequisites
- Access to GitHub Copilot. See What is GitHub Copilot?.
- Visual Studio 2022 version 17.8 or later. See Install Visual Studio in the Visual Studio documentation.
- GitHub Copilot extension. See Install GitHub Copilot in Visual Studio in the Visual Studio documentation.
- GitHub Copilot Chat extension. See Install GitHub Copilot in Visual Studio in the Visual Studio documentation.
- Sign in to GitHub in Visual Studio. If you experience authentication issues, see Troubleshooting issues with GitHub Copilot Chat in IDEs.
If you have access to GitHub Copilot via your organization, you won't be able to use GitHub Copilot Chat if your organization owner has disabled chat. See Managing policies for Copilot in your organization.
Submitting prompts
You can ask Copilot Chat to give code suggestions, explain code, generate unit tests, and suggest code fixes.
-
In the Visual Studio menu bar, click View, then click GitHub Copilot Chat.
-
In the Copilot Chat window, enter a prompt, then press Enter. For example prompts, see Getting started with prompts for Copilot Chat.
-
Evaluate Copilot's response, and submit a follow up prompt if needed.
The response often includes interactive elements. For example, the response may include buttons to copy, insert, or preview the result of a code block.
To see the files that Copilot Chat used to generate the response, click the References link below the response. The references may include a link to a custom instructions file for your repository. This file contains additional information that is automatically added to all of your chat questions to improve the quality of the responses. For more information, see Adding repository custom instructions for GitHub Copilot.
Using keywords in your prompt
You can use special keywords to help Copilot understand your prompt.
Extending Copilot Chat
GitHub Copilot Extensions integrate the power of external tools into Copilot Chat, helping you reduce context switching and receive responses with domain-specific context. You can install Copilot Extensions from the GitHub Marketplace or build private ones within your organization, then type @ in a chat window to see a list of your available extensions. To use an extension, select the extension from the list or type the full slug name, then type your prompt.
To learn more, see Using extensions to integrate external tools with Copilot Chat.
Slash commands
Use slash commands to avoid writing complex prompts for common scenarios. To use a slash command, type / in the chat prompt box, followed by a command.
To see all available slash commands, type / in the chat prompt box. See also GitHub Copilot Chat cheat sheet or Slash commands in the Visual Studio documentation.
References
By default, Copilot Chat will reference the file that you have open or the code that you have selected. You can also use # followed by a file name, file name and line numbers, or solution to reference a specific file, lines, or solution.
See also GitHub Copilot Chat cheat sheet or Reference in the Visual Studio documentation.
Using GitHub skills for Copilot (preview)
Note
The @github chat participant is currently in preview, and only available in Visual Studio 2022 Preview 2 onwards.
Copilot's GitHub-specific skills expand the type of information Copilot can provide. To access these skills in Copilot Chat in Visual Studio, include @github in your question.
When you add @github to a question, Copilot dynamically selects an appropriate skill, based on the content of your question. You can also explicitly ask Copilot Chat to use a particular skill. For example, @github Search the web to find the latest GPT4 model from OpenAI.
You can generate a list of currently available skills by asking Copilot: @github What skills are available?
AI models for Copilot Chat
You can change the large language model that Copilot uses to generate responses to chat prompts. You may find that different models perform better, or provide more useful responses, depending on the type of questions you ask. For more information see Changing the AI model for Copilot Chat.
Additional ways to access Copilot Chat
In addition to submitting prompts through the chat window, you can submit prompts inline. To start an inline chat, right click in your editor window and select Ask Copilot.
See Ask questions in the inline chat view in the Visual Studio documentation for more details.
Sharing feedback
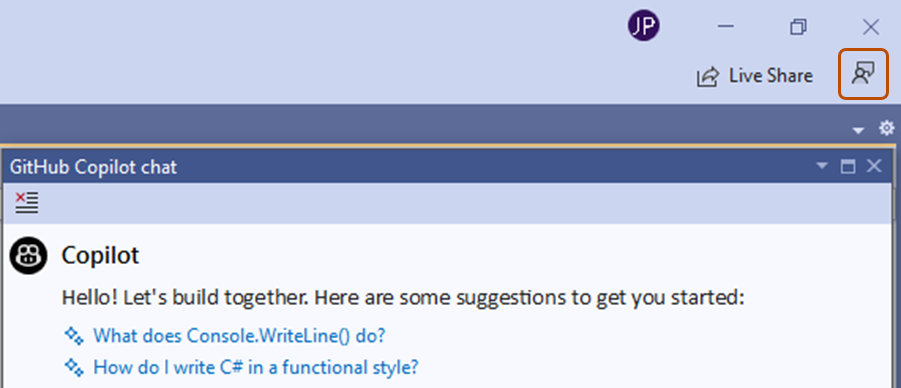
To share feedback about Copilot Chat, you can use the Send feedback button in Visual Studio. For more information on providing feedback for Visual Studio, see the Visual Studio Feedback documentation.
-
In the top right corner of the Visual Studio window, click the Send feedback button.
-
Choose the option that best describes your feedback.
- To report a bug, click Report a problem.
- To request a feature, click Suggest a feature.
Further reading
- Prompt engineering for Copilot Chat
- Using GitHub Copilot Chat in Visual Studio in the Microsoft Learn documentation
- Tips to improve GitHub Copilot Chat results in the Microsoft Learn documentation
- Asking GitHub Copilot questions in GitHub
- Responsible use of GitHub Copilot Chat in your IDE
- GitHub Terms for Additional Products and Features
- GitHub Copilot Trust Center
- GitHub Copilot FAQ
Prerequisites
-
Access to GitHub Copilot. See What is GitHub Copilot?.
-
A compatible JetBrains IDE. GitHub Copilot is compatible with the following IDEs:
- IntelliJ IDEA (Ultimate, Community, Educational)
- Android Studio
- AppCode
- CLion
- Code With Me Guest
- DataGrip
- DataSpell
- GoLand
- JetBrains Client
- MPS
- PhpStorm
- PyCharm (Professional, Community, Educational)
- Rider
- RubyMine
- RustRover
- WebStorm
- Writerside
See the JetBrains IDEs tool finder to download.
-
GitHub Copilot plugin. See the GitHub Copilot plugin in the JetBrains Marketplace. For installation instructions, see Installing the GitHub Copilot extension in your environment.
-
Log in to GitHub in your JetBrains IDE. For authentication instructions, see Installing the GitHub Copilot extension in your environment.
If you have access to GitHub Copilot via your organization, you won't be able to use GitHub Copilot Chat if your organization owner has disabled chat. See Managing policies for Copilot in your organization.
Submitting prompts
You can ask Copilot Chat to give code suggestions, explain code, generate unit tests, and suggest code fixes.
-
Open the Copilot Chat window by clicking the Copilot Chat icon at the right side of the JetBrains IDE window.

-
Enter a prompt in the prompt box. For example prompts, see Getting started with prompts for Copilot Chat.
-
Evaluate Copilot's response, and submit a follow up prompt if needed.
The response often includes interactive elements. For example, the response may include buttons to copy or insert a code block.
To see the files that Copilot Chat used to generate the response, select the References dropdown below the response.
Using keywords in your prompt
You can use special keywords to help Copilot understand your prompt.
Chat participants
Chat participants are like domain experts who have a specialty that they can help you with. You can use a chat participant to scope your prompt to a specific domain. To do this, type @ in the chat prompt box, followed by a chat participant name.
For a list of available chat participants, type @ in the chat prompt box. See also GitHub Copilot Chat cheat sheet.
Extending Copilot Chat
GitHub Copilot Extensions integrate the power of external tools into Copilot Chat, helping you reduce context switching and receive responses with domain-specific context. You can install Copilot Extensions from the GitHub Marketplace or build private ones within your organization, then type @ in a chat window to see a list of your available extensions. To use an extension, select the extension from the list or type the full slug name, then type your prompt.
To learn more, see Using extensions to integrate external tools with Copilot Chat.
Slash commands
Use slash commands to avoid writing complex prompts for common scenarios. To use a slash command, type / in the chat prompt box, followed by a command.
To see all available slash commands, type / in the chat prompt box. See also GitHub Copilot Chat cheat sheet
File references
By default, Copilot Chat will reference the file that you have open or the code that you have selected. You can also tell Copilot Chat which files to reference by dragging a file into the chat prompt box. Alternatively, you can right click on a file, select GitHub Copilot, then select Reference File in Chat.
Using GitHub skills for Copilot
Copilot's GitHub-specific skills expand the type of information Copilot can provide. To access these skills in Copilot Chat, include @github in your question.
When you add @github to a question, Copilot dynamically selects an appropriate skill, based on the content of your question. You can also explicitly ask Copilot Chat to use a particular skill. You can do this in two ways:
- Use natural language to ask Copilot Chat to use a skill. For example,
@github Search the web to find the latest GPT model from OpenAI. - To specifically invoke a web search you can include the
#webvariable in your question. For example,@github #web What is the latest LTS of Node.js?
You can generate a list of currently available skills by asking Copilot: @github What skills are available?
Additional ways to access Copilot Chat
- Built-in requests. In addition to submitting prompts through the chat window, you can submit built-in requests by right clicking in a file, selecting GitHub Copilot, then selecting one of the options.
- Inline. You can submit a chat prompt inline, and scope it to a highlighted code block or your current file.
- To start an inline chat, right click on a code block or anywhere in your current file, hover over GitHub Copilot, then select Copilot: Inline Chat, or enter Ctrl+Shift+I.
Sharing feedback
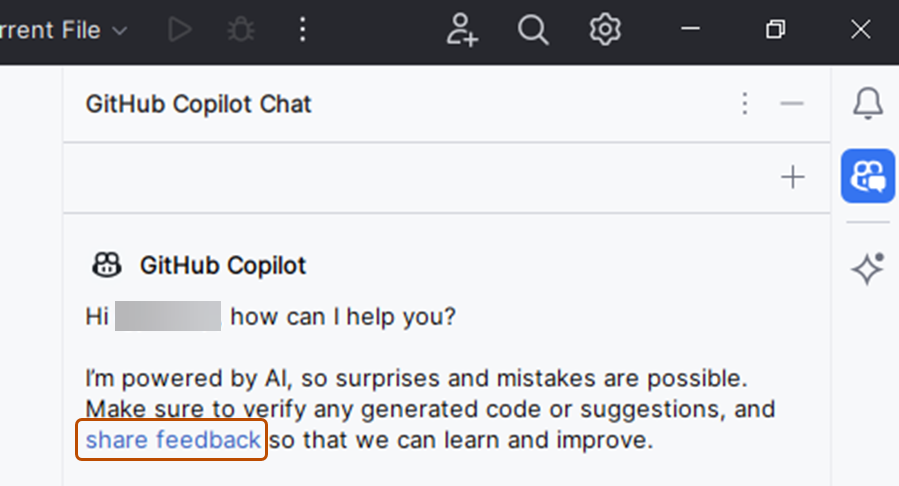
To share feedback about Copilot Chat, you can use the share feedback link in JetBrains.
-
At the right side of the JetBrains IDE window, click the Copilot Chat icon to open the Copilot Chat window.

-
At the top of the Copilot Chat window, click the share feedback link.
Further reading
Note
Copilot Chat in Xcode is in public preview and subject to change.
Prerequisites
To use GitHub Copilot for Xcode, you must install the GitHub Copilot for Xcode extension. See Installing the GitHub Copilot extension in your environment.
If you have access to GitHub Copilot via your organization, you won't be able to use GitHub Copilot Chat if your organization owner has disabled chat. See Managing policies for Copilot in your organization.
Submitting prompts
You can ask Copilot Chat to give code suggestions, explain code, generate unit tests, and suggest code fixes.
-
To open the chat view, click Copilot in the menu bar, then click Open Chat.
-
Enter a prompt in the prompt box. For example prompts, see Getting started with prompts for Copilot Chat.
-
Evaluate Copilot's response, and submit a follow up prompt if needed.
The response often includes interactive elements. For example, the response may include buttons to copy or insert a code block.
Using keywords in your prompt
You can use special keywords to help Copilot understand your prompt.
Slash commands
Use slash commands to avoid writing complex prompts for common scenarios. To use a slash command, type / in the chat prompt box, followed by a command.
To see all available slash commands, type / in the chat prompt box. For more information, see GitHub Copilot Chat cheat sheet.
File references
By default, Copilot Chat will reference the file that you have open or the code that you have selected. To attach a specific file as reference, click in the chat prompt box.
Chat management
You can open a conversation thread for each Xcode IDE to keep discussions organized across different contexts. You can also revisit previous conversations and reference past suggestions through the chat history.
Sharing feedback
To indicate whether a response was helpful, use or that appear next to the response.