Adding a file to a repository on GitHub
Files that you add to a repository via a browser are limited to 25 MiB per file. You can add larger files, up to 100 MiB each, via the command line. For more information, see Adding a file to a repository using the command line. To add files larger than 100 MiB, you must use Git Large File Storage. For more information, see About large files on GitHub.
You can upload multiple files to GitHub at the same time.
If a repository has any protected branches, you can't edit or upload files in the protected branch using GitHub. You can use GitHub Desktop to move your changes to a new branch and commit them. For more information, see About protected branches and Committing and reviewing changes to your project in GitHub Desktop.
Your repository may have push rulesets enabled. Push rulesets may block creating a new file in the repository based on certain restrictions. Push rulesets apply to the repository's entire fork network. Which means that any push rulesets that are configured in the root repository will also apply to every fork of the repository. For more information, see About rulesets.
Your repository may be secured by push protection. With push protection, GitHub will block uploading a file to the repository if the file contains a supported secret, such as a token. You should remove the secret from the file before attempting to upload the file again. For more information, see Working with push protection in the GitHub UI and Working with push protection in the GitHub UI.
Note
Push protection for file uploads in the web UI is currently in public preview and subject to change.
-
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
-
Above the list of files, select the Add file dropdown menu and click Upload files. Alternatively, you can drag and drop files into your browser.

-
To select the files you want to upload, drag and drop the file or folder, or click choose your files.
-
In the "Commit message" field, type a short, meaningful commit message that describes the change you made to the file. You can attribute the commit to more than one author in the commit message. For more information, see Creating a commit with multiple authors.
-
Below the commit message fields, decide whether to add your commit to the current branch or to a new branch. If your current branch is the default branch, you should choose to create a new branch for your commit and then create a pull request. For more information, see Creating a pull request.
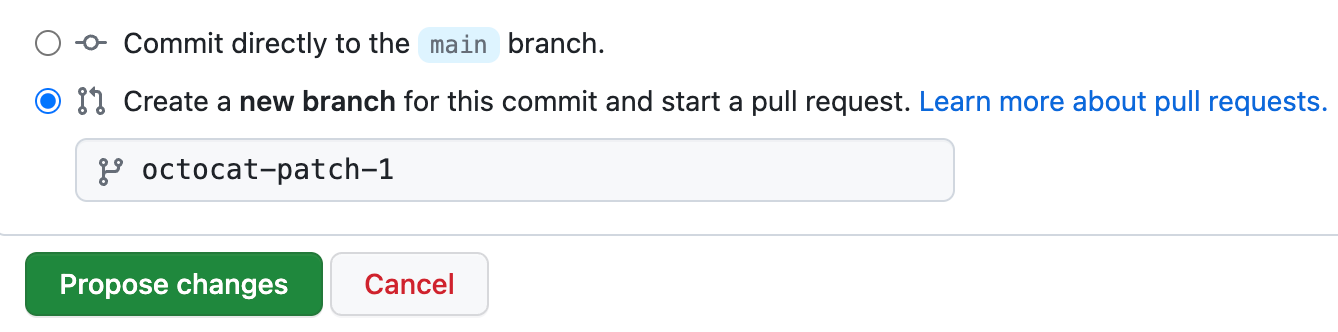
-
Click Propose changes.
Adding a file to a repository using the command line
You can upload an existing file to a repository on GitHub using the command line.
Tip
You can also add an existing file to a repository from the GitHub website.
This procedure assumes you've already:
- Created a repository on GitHub, or have an existing repository owned by someone else you'd like to contribute to
- Cloned the repository locally on your computer
Warning
Never git add, commit, or push sensitive information, for example passwords or API keys, to a remote repository. If you've already added this information, see Removing sensitive data from a repository.
-
On your computer, move the file you'd like to upload to GitHub into the local directory that was created when you cloned the repository.
-
Open Terminal.
-
Change the current working directory to your local repository.
-
Stage the file for commit to your local repository.
$ git add . # Adds the file to your local repository and stages it for commit. To unstage a file, use 'git reset HEAD YOUR-FILE'. -
Commit the file that you've staged in your local repository.
$ git commit -m "Add existing file" # Commits the tracked changes and prepares them to be pushed to a remote repository. To remove this commit and modify the file, use 'git reset --soft HEAD~1' and commit and add the file again. -
Push the changes in your local repository to GitHub.com.
$ git push origin YOUR_BRANCH # Pushes the changes in your local repository up to the remote repository you specified as the origin