Renaming a file on GitHub
Renaming a file also gives you the opportunity to move the file to a new location.
Tip
- If you try to rename a file in a repository that you don’t have access to, we will fork the project to your personal account and help you send a pull request to the original repository after you commit your change.
- File names created via the web interface can only contain alphanumeric characters and hyphens (
-). To use other characters, create and commit the files locally and then push them to the repository. - Some files, such as images, require that you rename them from the command line. For more information, see Renaming a file using the command line.
-
In your repository, browse to the file you want to rename.
-
In the upper right corner of the file view, click to open the file editor.

-
In the filename field, change the name of the file to the new filename you want. You can also update the contents of your file at the same time.

-
Click Commit changes...
-
In the "Commit message" field, type a short, meaningful commit message that describes the change you made to the file. You can attribute the commit to more than one author in the commit message. For more information, see Creating a commit with multiple authors.
-
Below the commit message fields, decide whether to add your commit to the current branch or to a new branch. If your current branch is the default branch, you should choose to create a new branch for your commit and then create a pull request. For more information, see Creating a pull request.
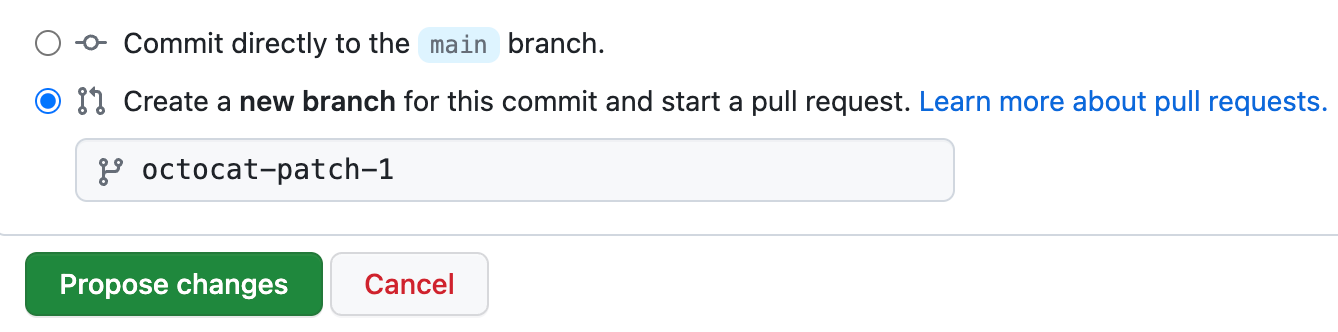
-
Click Commit changes or Propose changes.
Renaming a file using the command line
You can use the command line to rename any file in your repository.
Many files can be renamed directly on GitHub, but some files, such as images, require that you rename them from the command line.
This procedure assumes you've already:
- Created a repository on GitHub, or have an existing repository owned by someone else you'd like to contribute to
- Cloned the repository locally on your computer
-
Open Terminal.
-
Change the current working directory to your local repository.
-
Rename the file, specifying the old file name and the new name you'd like to give the file. This will stage your change for commit.
git mv OLD-FILENAME NEW-FILENAME -
Use
git statusto check the old and new file names.$ git status > # On branch YOUR-BRANCH > # Changes to be committed: > # (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage) > # > # renamed: OLD-FILENAME -> NEW-FILENAME > # -
Commit the file that you've staged in your local repository.
$ git commit -m "Rename file" # Commits the tracked changes and prepares them to be pushed to a remote repository. # To remove this commit and modify the file, use 'git reset --soft HEAD~1' and commit and add the file again. -
Push the changes in your local repository to your GitHub Enterprise Server instance.
$ git push origin YOUR_BRANCH # Pushes the changes in your local repository up to the remote repository you specified as the origin