You can create default issue templates and a default configuration file for issue templates for your organization or personal account. For more information, see "Creating a default community health file."
Creating issue templates
-
On your GitHub Enterprise Server instance, navigate to the main page of the repository.
-
Under your repository name, click Settings. If you cannot see the "Settings" tab, select the dropdown menu, then click Settings.

-
In the "Features" section, under Issues, click Set up templates. You may need to enable Issues and refresh the page before you can see the button.
-
Use the Add template dropdown menu, and click on the type of template you'd like to create.
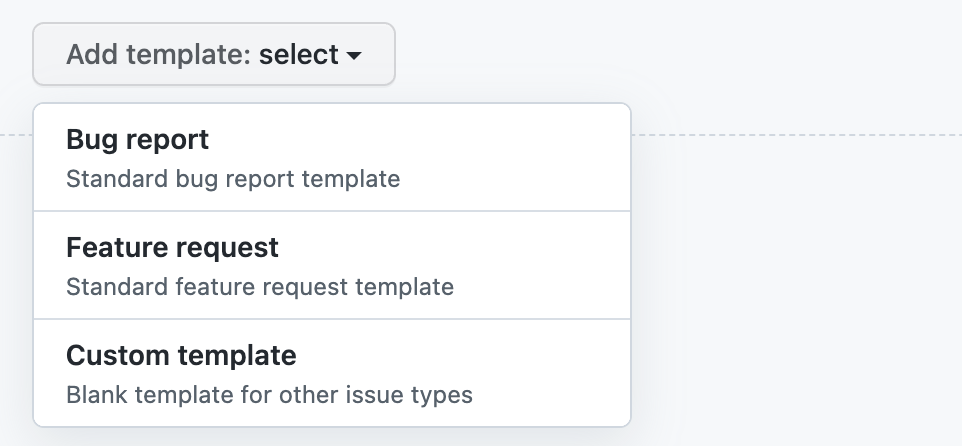
-
To preview or edit the template before committing it to the repository, next to the template, click Preview and edit.
-
To edit the template, click , and type in the fields to edit their contents.
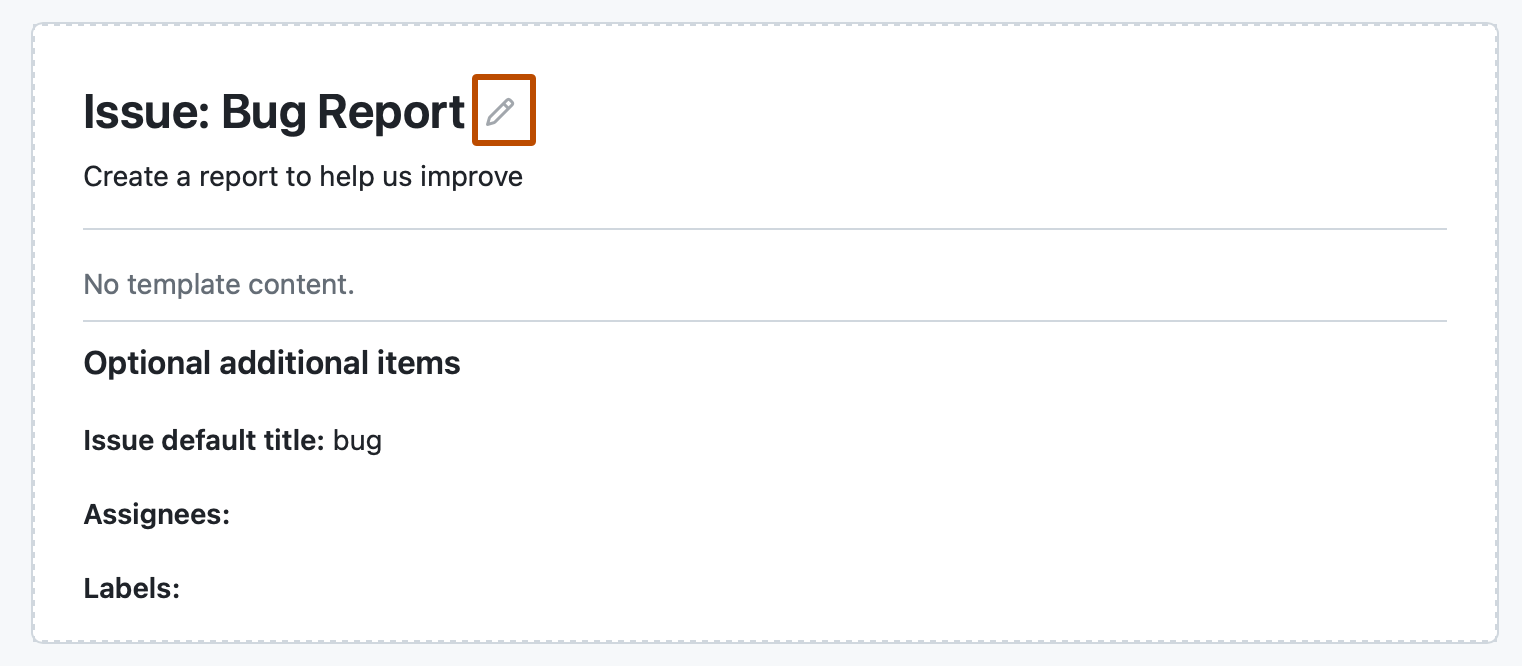
-
To automatically set a default issue title, assign the issue to people with read access to the repository, or apply labels to issues raised from the template, use the fields under "Optional additional information." You can also add these details in the issue template with
title,labels, orassigneesin a YAML frontmatter format. -
When you're finished editing and previewing your template, click Propose changes in the upper right corner of the page.
-
In the "Commit message" field, type a commit message describing your changes.
-
Below the commit message fields, select whether to commit your template directly to the default branch, or to create a new branch and open a pull request. For more information about pull requests, see "About pull requests."
-
Click Commit changes. Once these changes are merged into the default branch, the template will be available for contributors to use when they open new issues in the repository.
Configuring the template chooser
You can customize the issue template chooser that people see when creating a new issue in your repository by adding a config.yml file to the .github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE folder.
You can encourage contributors to use issue templates by setting blank_issues_enabled to false. If you set blank_issues_enabled to true, people will have the option to open a blank issue.
Note: If you used the legacy workflow to manually create an issue_template.md file in the .github folder and enable blank issues in your config.yml file, the template in issue_template.md will be used when people chose to open a blank issue. If you disable blank issues, the template will never be used.
If you prefer to receive certain reports outside of GitHub Enterprise Server, you can direct people to external sites with contact_links.
Here is an example config.yml file.
blank_issues_enabled: false
contact_links:
- name: GitHub Community Support
url: https://github.com/orgs/community/discussions
about: Please ask and answer questions here.
- name: GitHub Security Bug Bounty
url: https://bounty.github.com/
about: Please report security vulnerabilities here.
blank_issues_enabled: false
contact_links:
- name: GitHub Community Support
url: https://github.com/orgs/community/discussions
about: Please ask and answer questions here.
- name: GitHub Security Bug Bounty
url: https://bounty.github.com/
about: Please report security vulnerabilities here.
Your configuration file will customize the template chooser when the file is merged into the repository's default branch.
-
On your GitHub Enterprise Server instance, navigate to the main page of the repository.
-
Above the list of files, using the Add file drop-down, click Create new file.
-
In the file name field, type
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/config.yml. -
In the body of the new file, type the contents of your configuration file.
-
In the "Commit message" field, type a short, meaningful commit message that describes the change you made to the file. You can attribute the commit to more than one author in the commit message. For more information, see "Creating a commit with multiple authors."
-
Below the commit message fields, decide whether to add your commit to the current branch or to a new branch. If your current branch is the default branch, you should choose to create a new branch for your commit and then create a pull request. For more information, see "Creating a pull request."
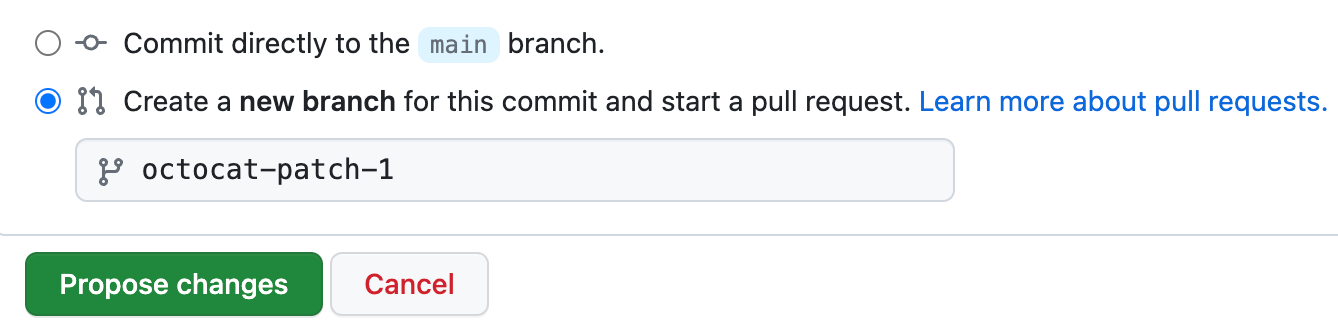
-
Click Commit changes or Propose changes.