About adding existing source code to GitHub Enterprise Server
If you have source code stored locally on your computer that is tracked by Git or not tracked by any version control system (VCS), you can add the code to GitHub Enterprise Server by typing commands in a terminal. You can do this by typing Git commands directly, or by using GitHub CLI.
GitHub CLI is an open source tool for using GitHub from your computer's command line. GitHub CLI can simplify the process of adding an existing project to GitHub Enterprise Server using the command line. To learn more about GitHub CLI, see "About GitHub CLI."
Note: If you're most comfortable with a point-and-click user interface, consider adding your project with GitHub Desktop instead. For more information, see "Adding a repository from your local computer to GitHub Desktop."
If your source code is tracked by a different VCS, such as Mercurial, Subversion, or Team Foundation Version Control, you must convert the repository to Git before you can add the project to GitHub Enterprise Server.
- "Importing a Subversion repository"
- "Importing a Mercurial repository"
- "Importing a Team Foundation Version Control repository"
Warning: Never git add, commit, or push sensitive information to a remote repository. Sensitive information can include, but is not limited to:
- Passwords
- SSH keys
- AWS access keys
- API keys
- Credit card numbers
- PIN numbers
For more information, see "Removing sensitive data from a repository."
Initializing a Git repository
If your locally-hosted code isn't tracked by any VCS, the first step is to initialize a Git repository. If your project is already tracked by Git, skip to "Importing a Git repository with the command line."
-
Open TerminalTerminalGit Bash.
-
Navigate to the root directory of your project.
-
Initialize the local directory as a Git repository. By default, the initial branch is called
main.If you’re using Git 2.28.0 or a later version, you can set the name of the default branch using
-b.git init -b mainIf you’re using Git 2.27.1 or an earlier version, you can set the name of the default branch using
git symbolic-ref.git init && git symbolic-ref HEAD refs/heads/main -
Add the files in your new local repository. This stages them for the first commit.
$ git add . # Adds the files in the local repository and stages them for commit. To unstage a file, use 'git reset HEAD YOUR-FILE'. -
Commit the files that you've staged in your local repository.
$ git commit -m "First commit" # Commits the tracked changes and prepares them to be pushed to a remote repository. To remove this commit and modify the file, use 'git reset --soft HEAD~1' and commit and add the file again.
Importing a Git repository with the command line
After you've initialized a Git repository, you can push the repository to GitHub Enterprise Server, using either GitHub CLI or Git.
- "Adding a local repository to GitHub with GitHub CLI"
- "Adding a local repository to GitHub using Git"
Adding a local repository to GitHub with GitHub CLI
-
To create a repository for your project on GitHub, use the
gh repo createsubcommand. When prompted, select Push an existing local repository to GitHub and enter the desired name for your repository. If you want your project to belong to an organization instead of your user account, specify the organization name and project name withorganization-name/project-name. -
Follow the interactive prompts. To add the remote and push the repository, confirm yes when asked to add the remote and push the commits to the current branch.
-
Alternatively, to skip all the prompts, supply the path to the repository with the
--sourceflag and pass a visibility flag (--public,--private, or--internal). For example,gh repo create --source=. --public. Specify a remote with the--remoteflag. To push your commits, pass the--pushflag. For more information about possible arguments, see the GitHub CLI manual.
Adding a local repository to GitHub using Git
Before you can add your local repository to GitHub using Git, you must authenticate to GitHub on the command line. For more information, see "About authentication to GitHub."
-
Create a new repository on your GitHub Enterprise Server instance. To avoid errors, do not initialize the new repository with README, license, or gitignore files. You can add these files after your project has been pushed to GitHub Enterprise Server. For more information, see "Creating a new repository."
-
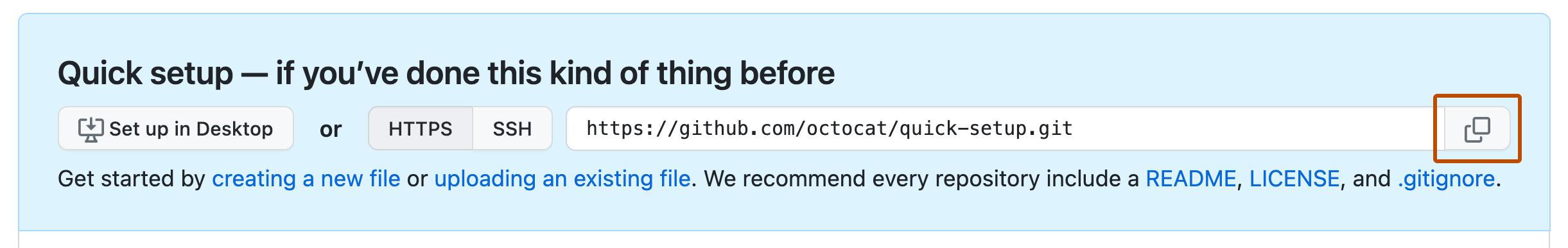
At the top of your repository on your GitHub Enterprise Server instance's Quick Setup page, click to copy the remote repository URL.
-
Open TerminalTerminalGit Bash.
-
Change the current working directory to your local project.
-
To add the URL for the remote repository where your local repository will be pushed, run the following command. Replace
REMOTE-URLwith the repository's full URL on GitHub.git remote add origin REMOTE-URLFor more information, see "Managing remote repositories."
-
To verify that you set the remote URL correctly, run the following command.
git remote -v -
To push the changes in your local repository to your GitHub Enterprise Server instance, run the following command.
git push -u origin mainIf your default branch is not named "main," replace "main" with the name of your default branch. For more information, see "About branches."
-
Create a new repository on your GitHub Enterprise Server instance. To avoid errors, do not initialize the new repository with README, license, or gitignore files. You can add these files after your project has been pushed to GitHub Enterprise Server. For more information, see "Creating a new repository."
-
At the top of your repository on your GitHub Enterprise Server instance's Quick Setup page, click to copy the remote repository URL.

-
Open TerminalTerminalGit Bash.
-
Change the current working directory to your local project.
-
To add the URL for the remote repository where your local repository will be pushed, run the following command. Replace
REMOTE-URLwith the repository's full URL on GitHub.git remote add origin REMOTE-URLFor more information, see "Managing remote repositories."
-
To verify that you set the remote URL correctly, run the following command.
git remote -v -
To push the changes in your local repository to your GitHub Enterprise Server instance, run the following command.
git push origin mainIf your default branch is not named "main," replace "main" with the name of your default branch. For more information, see "About branches."
-
Create a new repository on your GitHub Enterprise Server instance. To avoid errors, do not initialize the new repository with README, license, or gitignore files. You can add these files after your project has been pushed to GitHub Enterprise Server. For more information, see "Creating a new repository."
-
At the top of your repository on your GitHub Enterprise Server instance's Quick Setup page, click to copy the remote repository URL.

-
Open TerminalTerminalGit Bash.
-
Change the current working directory to your local project.
-
To add the URL for the remote repository where your local repository will be pushed, run the following command. Replace
REMOTE-URLwith the repository's full URL on GitHub.git remote add origin REMOTE-URLFor more information, see "Managing remote repositories."
-
To verify that you set the remote URL correctly, run the following command.
git remote -v -
To push the changes in your local repository to your GitHub Enterprise Server instance, run the following command.
git push origin mainIf your default branch is not named "main," replace "main" with the name of your default branch. For more information, see "About branches."