注意:GitHub Enterprise Server 目前不支持 GitHub 托管的运行器。 可以在 GitHub public roadmap 上查看有关未来支持计划的更多信息。
简介
本指南演示如何将 PowerShell 用于 CI。 它介绍了如何使用 Pester、安装依赖项、测试模块以及发布到 PowerShell Gallery。
GitHub 托管的运行器具有预安装了软件的工具缓存,包括 PowerShell 和 Pester。
有关最新软件和 PowerShell 和 Pester 预装版本的完整列表,请参阅“使用 GitHub 托管的运行器”。
先决条件
您应该熟悉 YAML 和 GitHub Actions 的语法。 有关详细信息,请参阅“了解 GitHub Actions”。
建议您对 PowerShell 和 Pester 有个基本的了解。 有关详细信息,请参阅:
在 GitHub Enterprise Server 上使用自托管的运行器
在包含自承载运行器的 GitHub Enterprise Server 上使用设置操作(例如 actions/setup-LANGUAGE)时,可能需要在无法访问 Internet 的运行器上设置工具缓存。 有关详细信息,请参阅“在未接入互联网的自托管运行器上设置工具缓存”。
为 Pester 添加工作流程
要使用 PowerShell 和 Pester 自动执行测试,您可以添加在每次将更改推送到仓库时运行的工作流程。 在以下示例中,Test-Path 用于检查名为 resultsfile.log 的文件是否存在。
必须将此示例工作流文件添加到存储库的 .github/workflows/ 目录:
name: Test PowerShell on Ubuntu
on: push
jobs:
pester-test:
name: Pester test
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Check out repository code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Perform a Pester test from the command-line
shell: pwsh
run: Test-Path resultsfile.log | Should -Be $true
- name: Perform a Pester test from the Tests.ps1 file
shell: pwsh
run: |
Invoke-Pester Unit.Tests.ps1 -Passthru
-
shell: pwsh- 将作业配置为在运行run命令时使用 PowerShell。 -
run: Test-Path resultsfile.log- 检查存储库的根目录中是否存在名为resultsfile.log的文件。 -
Should -Be $true- 使用 Pester 定义预期结果。 如果结果是非预期的,则 GitHub Actions 会将此标记为失败的测试。 例如: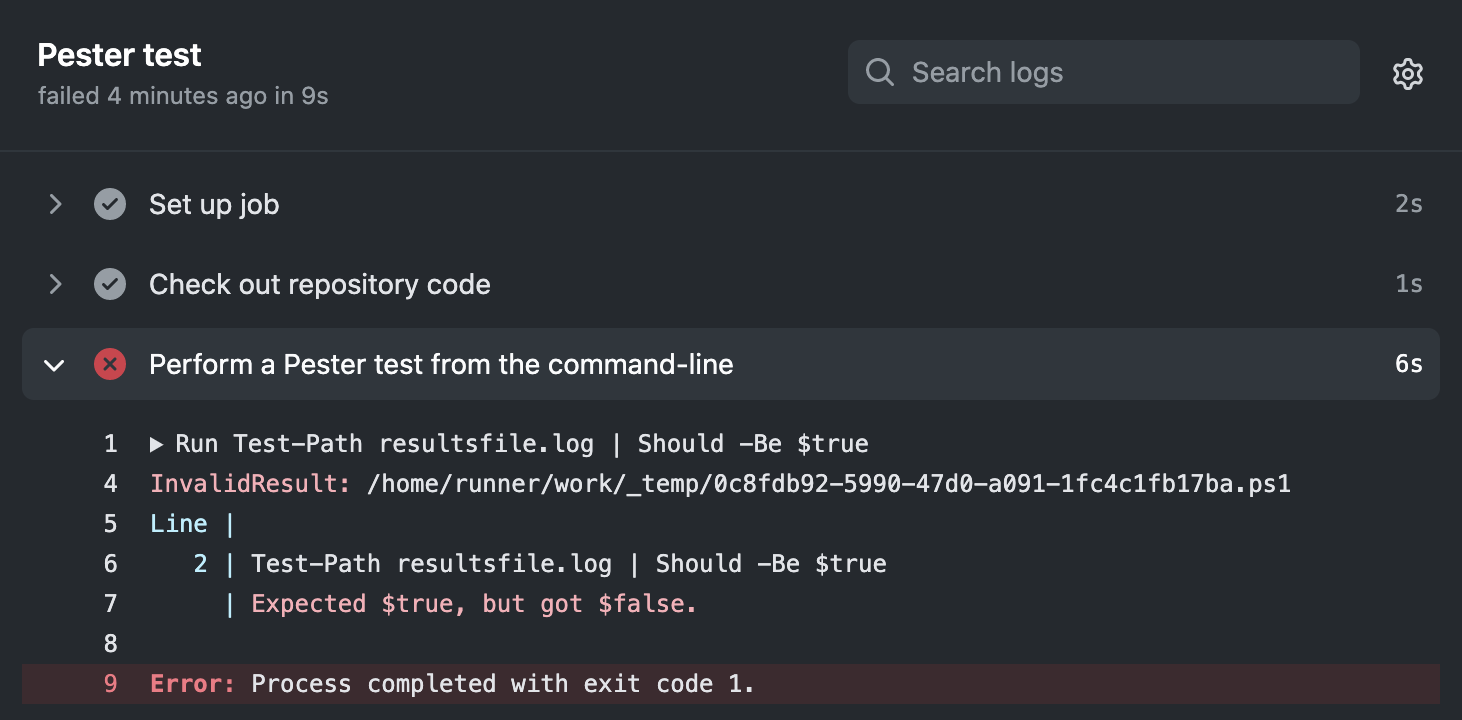
-
Invoke-Pester Unit.Tests.ps1 -Passthru- 使用 Pester 执行在名为Unit.Tests.ps1的文件中定义的测试。 例如,若要执行上述相同的测试,Unit.Tests.ps1将包含以下命令:Describe "Check results file is present" { It "Check results file is present" { Test-Path resultsfile.log | Should -Be $true } }
PowerShell 模块位置
下表描述了每个 GitHub 托管的运行器中各个 PowerShell 模块的位置。
| Ubuntu | macOS | Windows | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PowerShell 系统模块 | /opt/microsoft/powershell/7/Modules/* | /usr/local/microsoft/powershell/7/Modules/* | C:\program files\powershell\7\Modules\* |
| PowerShell 加载项模块 | /usr/local/share/powershell/Modules/* | /usr/local/share/powershell/Modules/* | C:\Modules\* |
| 用户安装的模块 | /home/runner/.local/share/powershell/Modules/* | /Users/runner/.local/share/powershell/Modules/* | C:\Users\runneradmin\Documents\PowerShell\Modules\* |
注意:在 Ubuntu 运行器上,Azure PowerShell 模块存储在 /usr/share/ 中,而不是 PowerShell 加载项模块的默认位置(即 /usr/local/share/powershell/Modules/)。
安装依赖关系
GitHub 托管的运行器安装了 PowerShell 7 和 Pester。 在生成和测试代码之前,可使用 Install-Module 从 PowerShell 库安装其他依赖项。
注意:由 GitHub 托管的运行器使用的预安装包(如 Pester)会定期更新,并且可能会引入重大更改。 因此,建议始终通过将 Install-Module 与 -MaximumVersion 结合使用来指定所需的包版本。
你还可以缓存依赖项以加快工作流。 有关详细信息,请参阅“缓存依赖项以加快工作流程”。
例如,以下作业安装 SqlServer 和 PSScriptAnalyzer 模块:
jobs:
install-dependencies:
name: Install dependencies
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Install from PSGallery
shell: pwsh
run: |
Set-PSRepository PSGallery -InstallationPolicy Trusted
Install-Module SqlServer, PSScriptAnalyzer
注意:默认情况下,PowerShell 不信任任何存储库。 从 PowerShell 库安装模块时,必须将 PSGallery 的安装策略显式设置为 Trusted。
缓存依赖项
可使用唯一的键来缓存 PowerShell 依赖项,这样就可以通过 cache 操作还原未来工作流的依赖项。 有关详细信息,请参阅“缓存依赖项以加快工作流程”。
PowerShell 根据运行器的操作系统将其依赖项缓存在不同的位置。 例如,对于 Windows 操作系统,以下 Ubuntu 示例中使用的 path 位置将有所不同。
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup PowerShell module cache
id: cacher
uses: actions/cache@v3
with:
path: "~/.local/share/powershell/Modules"
key: ${{ runner.os }}-SqlServer-PSScriptAnalyzer
- name: Install required PowerShell modules
if: steps.cacher.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
shell: pwsh
run: |
Set-PSRepository PSGallery -InstallationPolicy Trusted
Install-Module SqlServer, PSScriptAnalyzer -ErrorAction Stop
测试代码
您可以使用与本地相同的命令来构建和测试代码。
使用 PSScriptAnalyzer 链接代码
以下示例安装 PSScriptAnalyzer 并使用它对存储库中的所有 ps1 文件执行 lint 操作。 有关详细信息,请参阅 GitHub 上的 PSScriptAnalyzer。
lint-with-PSScriptAnalyzer:
name: Install and run PSScriptAnalyzer
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Install PSScriptAnalyzer module
shell: pwsh
run: |
Set-PSRepository PSGallery -InstallationPolicy Trusted
Install-Module PSScriptAnalyzer -ErrorAction Stop
- name: Lint with PSScriptAnalyzer
shell: pwsh
run: |
Invoke-ScriptAnalyzer -Path *.ps1 -Recurse -Outvariable issues
$errors = $issues.Where({$_.Severity -eq 'Error'})
$warnings = $issues.Where({$_.Severity -eq 'Warning'})
if ($errors) {
Write-Error "There were $($errors.Count) errors and $($warnings.Count) warnings total." -ErrorAction Stop
} else {
Write-Output "There were $($errors.Count) errors and $($warnings.Count) warnings total."
}
将工作流数据打包为构件
您可以在工作流程完成后上传构件以查看。 例如,您可能需要保存日志文件、核心转储、测试结果或屏幕截图。 有关详细信息,请参阅“将工作流程数据存储为构件”。
以下示例演示如何使用 upload-artifact 操作来存档从 Invoke-Pester 收到的测试结果。 有关详细信息,请参阅 upload-artifact 操作。
name: Upload artifact from Ubuntu
on: [push]
jobs:
upload-pester-results:
name: Run Pester and upload results
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Test with Pester
shell: pwsh
run: Invoke-Pester Unit.Tests.ps1 -Passthru | Export-CliXml -Path Unit.Tests.xml
- name: Upload test results
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
with:
name: ubuntu-Unit-Tests
path: Unit.Tests.xml
if: ${{ always() }}
always() 函数将作业配置为即使存在测试失败也要继续处理。 有关详细信息,请参阅“上下文”。
发布到 PowerShell Gallery
您可以配置工作流程在 CI 测试通过时将 PowerShell 模块发布到 PowerShell Gallery。 您可以使用机密来存储发布软件包所需的任何令牌或凭据。 有关详细信息,请参阅“在 GitHub Actions 中使用机密”。
以下示例创建一个包并使用 Publish-Module 将其发布到 PowerShell 库:
name: Publish PowerShell Module
on:
release:
types: [created]
jobs:
publish-to-gallery:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Build and publish
env:
NUGET_KEY: ${{ secrets.NUGET_KEY }}
shell: pwsh
run: |
./build.ps1 -Path /tmp/samplemodule
Publish-Module -Path /tmp/samplemodule -NuGetApiKey $env:NUGET_KEY -Verbose