Use a load balancer in front of a single GitHub Enterprise appliance or a pair of appliances in a High Availability configuration.
A load balancer design uses a network device to direct Git and HTTP traffic to individual GitHub Enterprise appliances. You can use a load balancer to restrict direct traffic to the appliance for security purposes or to redirect traffic if needed without DNS record changes. We strongly recommend a TCP load balancer.
DNS lookups for the GitHub Enterprise hostname should resolve to the load balancer. If subdomain isolation is enabled (recommended), an additional wildcard record (*.[hostname]) should also resolve to the load balancer. For more information, see "About subdomain isolation."
Warning: Terminating TLS at a load balancer is not supported. When using TLS (which is recommended), HTTPS traffic must be forwarded directly to the appliance without modification.
Handling client connection information
Because client connections to GitHub Enterprise come from the load balancer, the client IP address can be lost. To properly capture the client connection information, additional consideration is required.
If your load balancer can support it, the preferred solution is the PROXY protocol. When no PROXY support is available, it is also possible to load balance the HTTP and HTTPS ports using the X-Forwarded-For header.
Security Warning: When either PROXY support or HTTP forwarding is enabled, it is critical that no external traffic can directly reach the GitHub Enterprise appliances. If external traffic is not properly blocked, it can allow the source IP addresses to be forged.
Enabling PROXY support on GitHub Enterprise
Enable PROXY support for both your appliance and the load balancer. Use the instructions provided by your vendor to enable the PROXY protocol on your load balancer.
In the upper-right corner of any page, click .
In the left sidebar, click Management Console.
In the left sidebar, click Privacy.
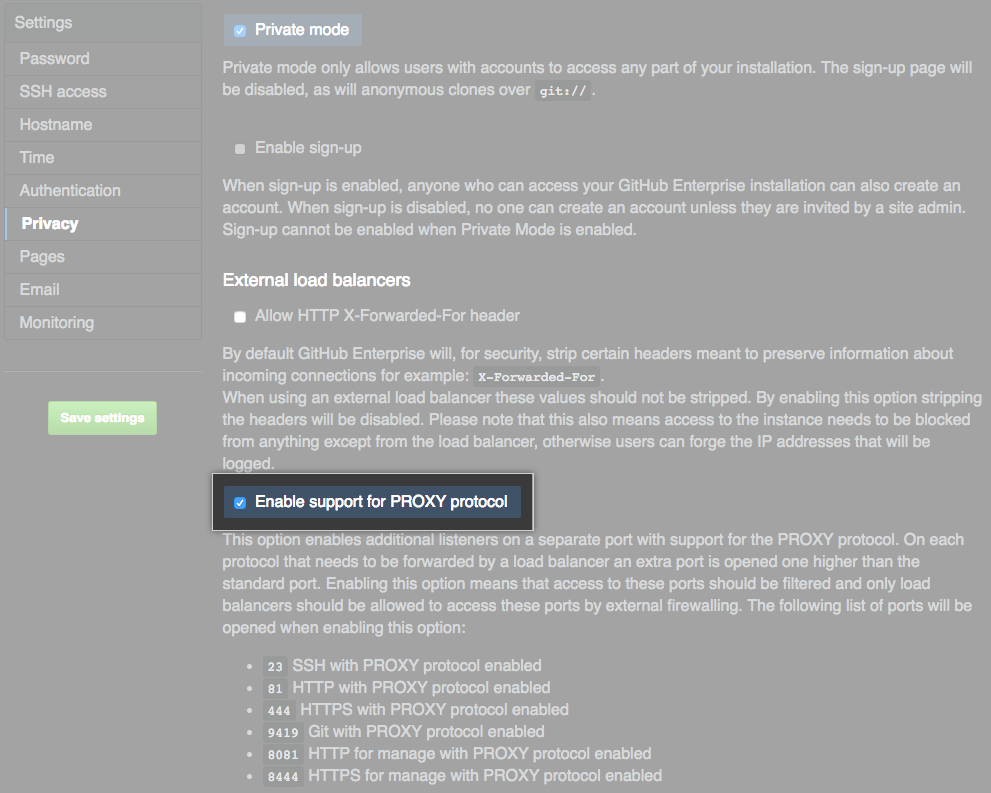
Under External load balancers, select Enable support for PROXY protocol.
- At the bottom of the Management Console configuration page, click Save settings.
PROXY protocol TCP port mappings
| Source Port | Destination Port | Service Description |
|---|---|---|
| 22 | 23 | Git over SSH |
| 80 | 81 | HTTP |
| 443 | 444 | HTTPS |
| 8080 | 8081 | Management Console HTTP |
| 8443 | 8444 | Management Console HTTPS |
| 9418 | 9419 | Git |
Enabling X-Forwarded-For support on GitHub Enterprise
The X-Fowarded-For header will only work with HTTP and HTTPS. The IP address reported for Git over SSH connections will show the load balancer IP.
In the upper-right corner of any page, click .

In the left sidebar, click Management Console.

In the left sidebar, click Privacy.

Under External load balancers, select Allow HTTP X-Forwarded-For header.
- At the bottom of the Management Console configuration page, click Save settings.

Protocol TCP port mappings for use without PROXY support
| Source Port | Destination Port | Service Description |
|---|---|---|
| 22 | 22 | Git over SSH |
| 25 | 25 | SMTP |
| 80 | 80 | HTTP |
| 443 | 443 | HTTPS |
| 8080 | 8080 | Management Console HTTP |
| 8443 | 8443 | Management Console HTTPS |
Configuring health checks
Health checks allow a load balancer to stop sending traffic to a node that is not responding if a pre-configured check fails on that node. If the appliance is offline due to maintenance or unexpected failure, the load balancer can display a status page. In a High Availability configuration it can be used as part of a failover strategy, however automatic failover of HA pairs is not supported. You must manually promote the replica appliance before it will begin serving requests. For more information, see the load balancer section in the High Availability configuration documentation.
Configure the load balancer to check one of these URLs:
-
https://<hostname>/statusif HTTPS is enabled (default). -
http://<hostname>/statusif HTTPS is disabled
The check will return status code 200 (OK) if the node is healthy and available to service end-user requests.
Warning: If you check the status URL using HTTP while HTTPS is enabled, it will redirect to HTTPS. This may cause the health check to fail.
Note: When the appliance is in maintenance mode, the https://<hostname>/status URL will return status code 503 (Service Unavailable). For more information, see "Enabling and scheduling maintenance mode."
